Corneal Topographers Are Used To Trace the Cornea's Curved Surface for Finding Indications of Underlying Eye Diseases
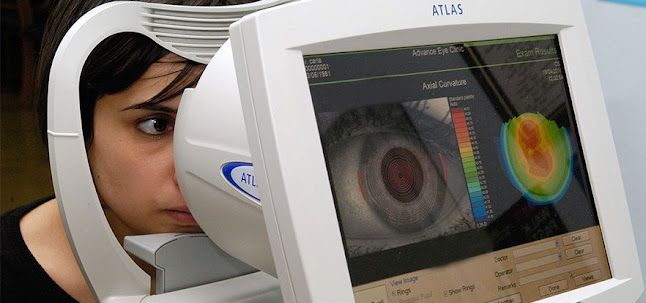
Corneal topographers, more commonly known as Photokeratoscopy, are a non-surgical medical imaging method used in regions such as the U.S., U.K. and Italy among others, for non-intravenous mapping of the corneal surface. Unlike conventional corneal topography, laser peripheral iridotomy is used to treat patients with myopia, hypermetropia, or astigmatism. The procedure involves the insertion of a thin fiber-optic laser into the central area of a cornea called the iris. The resulting corneal flap is used as a guide for treating the affected areas to improve vision. In conventional corneal topographers (x-ray or tomography), light is emitted on the corneal surface from the focused laser beam. As the light passes through the corneal tissue, the irregularities in the corneal surface are observed by reflected light. This image provides information about the internal microcosm and the optical properties of the corneal layer. The main advantage of corneal topographers is that they can...