Corneal Topographers Are Used To Trace the Cornea's Curved Surface for Finding Indications of Underlying Eye Diseases
Corneal topographers,
more commonly known as Photokeratoscopy, are a non-surgical medical imaging
method used in regions such as the U.S., U.K. and Italy among others, for
non-intravenous mapping of the corneal surface. Unlike conventional corneal
topography, laser peripheral iridotomy is used to treat patients with myopia,
hypermetropia, or astigmatism. The procedure involves the insertion of a thin
fiber-optic laser into the central area of a cornea called the iris. The
resulting corneal flap is used as a guide for treating the affected areas to
improve vision.
In conventional corneal
topographers (x-ray or tomography), light is emitted on the corneal surface
from the focused laser beam. As the light passes through the corneal tissue,
the irregularities in the corneal surface are observed by reflected light. This
image provides information about the internal microcosm and the optical
properties of the corneal layer. The main advantage of corneal topographers is
that they can provide detailed images of the microstructure of a small region
of interest while using a low-energy laser rather than a conventional x-ray
lamp. It enables the detection of unusual glaucoma or other eye diseases before
they progress to retinal detachment.
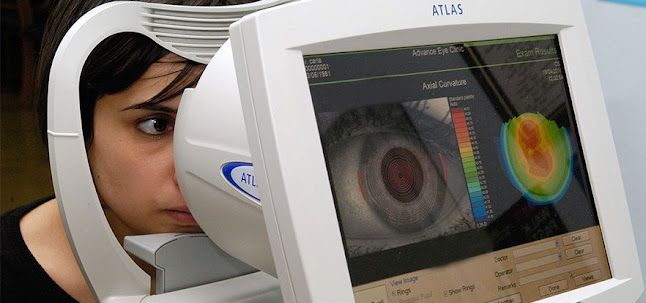
The objective of
corneal topographers is to create a three-dimensional picture of the corneal
surface in a clear and picturesque manner. The first step of this technique is
the generation of corneal topographers by injecting light in a particular
pattern that will generate a reflection in the corneal tissue. As the light
travels through the corneal flap, it causes refraction of the incoming light so
that it appears as a sharp point on the corneal surface. After the injection of
the light, a change in the permeability of the corneal topography will cause
characteristic changes in the light wave that reflects on the corneal surface.
In a region such as the United States, owing to increased screen timing and
choice of personal, issues related to eye care are the maximum. For instance,
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, around 93 million
adults in the U.S. are highly vulnerable to serious vision loss.



Comments
Post a Comment