Europe Needle-free IV Connectors; Help Reduce the Risk of Blood Stream Infections and Needle-Stick Injuries
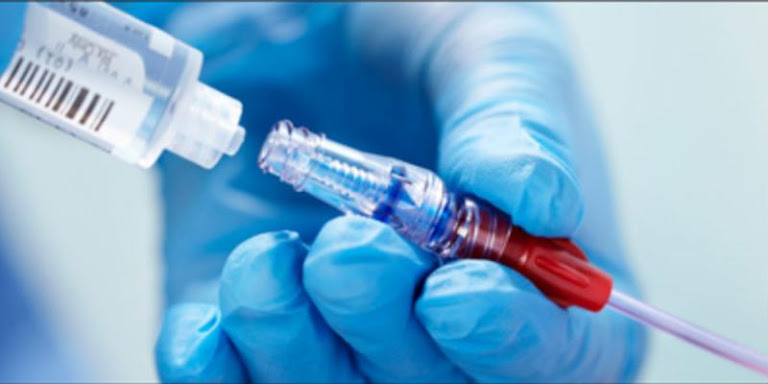
Europe needle-free IV connectors are medical devices that
connect to the end of vascular catheters and enable catheter access for
infusion and aspiration. Various different designs of needle-free IV connectors
are available, making it difficult to identify the features that present the
least risk and greatest safety. In the hospitals, these medical devices are
widely used for intravenous administration of drugs and fluids to protect the
central part of the vascular access systems. Needle-free IV connectors help
reduce the risk of potential contaminants associated with IV administration and
prevent manipulation of all types of IV infections.
Moreover, Europe
needle-free IV connectors help reduce the risk of needle-stick
injuries, and thus reduces the risk of blood borne infectious diseases. Furthermore,
advancements in needle-free IV connectors, such as connectors embedded with
antimicrobial agents, closed IV systems, and connectors preventing fluid
reflux, are expected reduce the risk of bloodstream infections linked to IV
administration. These connectors are suitable for all central, arterial, and
peripheral venous catheters for the administration of drugs and fluids to
patients.
Many government organizations or regulatory bodies have also
recommended the usage of these connectors to reduce the risk of blood stream
infections and needle-stick injuries. Needle-free connectors have three
different mechanism of action, such as neutral fluid displacement, negative
fluid displacement, and positive fluid displacement. With the increasing incidence
of needle-stick injuries & catheter-related bloodstream infections, the
demand for Europe needle-free IV connectors is also increasing. According to
the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (2018 report), each year, around
1 million needle stick injuries occur in Europe.
Moreover, a study in Germany university hospital showed that
31.4% of health care workers sustained at least one needle stick injury in one
year. Most of these injuries occur during disposal of used syringes and
recapping.



Comments
Post a Comment