PARP inhibitors: its role in treatment of cancer
PARP is a significant protein in DNA fix pathways
particularly the base extraction fix (BER). BER is engaged with DNA fix of
single strand breaks (SSBs). On the off chance that BER is impeded, restraining
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), SSBs collect and become twofold stand
breaks (DSBs). The cells with expanding number of DSBs become more subject to
other fix pathways, mostly the homologous recombination (HR) and the
nonhomologous end joining. Patients with faulty HR, as BRCA-lacking cell lines,
are much more vulnerable to debilitation of the BER pathway. Inhibitors of PARP
specially murder malignant growth cells in BRCA-transformation disease cell
lines over typical cells. Likewise, PARP inhibitors increment cytotoxicity by
restraining fix within the sight of chemotherapies that actuates SSBs. These
two standards have been tried clinically. Throughout the most recent couple of
years, fervor over this class of specialists has heightened because of detailed
action as single specialist in BRCA1-or BRCA2-related ovarian or bosom
diseases, and in mix with chemotherapy in triple negative bosom malignancy.
This audit covers the current consequences of clinical preliminaries testing
those two standards. It likewise assesses future headings for the field of PARP
inhibitor improvement.
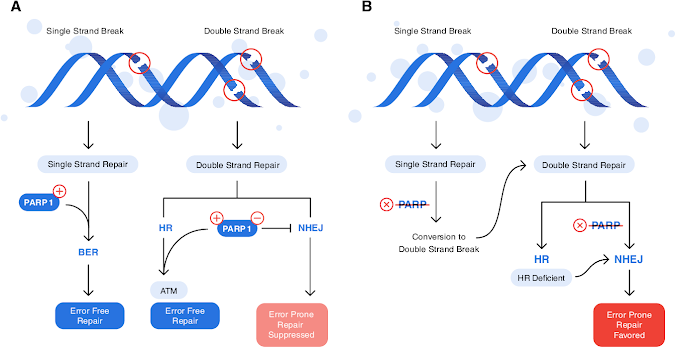
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) is a significant
protein in the base extraction fix (BER) pathway for DNA single strand breaks
(SSBs). This makes PARP1 an intriguing objective for malignancy treatment. At
present there are eight PARP inhibitors in clinical advancement testing two
ideas. One applies the manufactured lethality head and tests single specialist PARP
inhibitor in patients with insufficient homologous recombination (HR)
like BRCA-transformation tumors. The other idea is to bargain the cells
capacity to fix DNA harm brought about by specific chemotherapies. The clinical
information are simply gradually developing and traces of action are found in
the BRCA-transformation malignancies and triple negative bosom disease (TNBC).
These early traces of exercises have prompted expectant fervor for this class
of specialists.
PARP is a group of proteins approximately dependent on
primary closeness and function[1]. PARP proteins are made out of two ribose
moieties and two phosphates for each unit polymer. PARP1 and PARP2 are
catalysts engaged with a DNA fix pathway for SSBs called BER. The most popular
PARP is PARP1 (Figure 1)[2]. This catalyst was first detailed in 1963[6]. In
1980 Durkacz et al. [7] recommended that adjusting PARP1 may increase the
impact of alkylator chemotherapy. PARP1 recognizes and ties to destinations of
single strand DNA harm by means of the DNA-restricting space. It at that point
orchestrates poly(ADP) ribose (PAR) and moves it to acceptor proteins. Standard
enlisted people other fix proteins to the harmed DNA site. On account of
outrageous DNA harm, similarly as with ischemia, PARP1 hyperactivation prompts
consumption of NAD+ and ATP, bringing about cell demise by rot or apoptosis.
Standard is associated with twofold strand breaks (DSBs) fix as well[8].
Standard volunteers ATM, MRE11, and topoisomerase 1, which are engaged with
DSBs fix
Read More : https://prn.to/3u8XWsA



Comments
Post a Comment