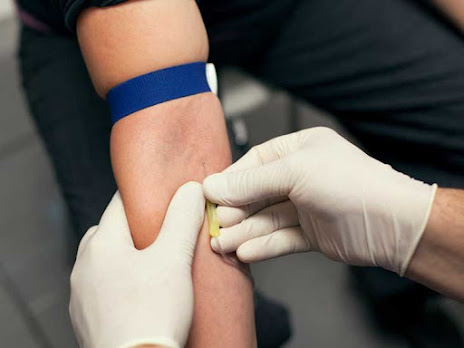
Xylose Absorption Test Is Done To Measure the Level of Xylose, a Type of Sugar
The Xylose absorption test (D-Xylose Absorption Test) is
used to measure the level of xylose in urine and blood to estimate an
individual’s capacity to absorb carbohydrates. It is used to diagnose
malabsorption, a disorder in which nutrients are not absorbed properly by the
small intestine. Xylose is a carbohydrate which is absorbed by the body. Xylose
absorption test helps to determine the malabsorption cause. Xylose, or D-Xylose,
is a type of sugar occurs naturally in cereals, fruits, and vegetables such as
potatoes, peas, and carrots.
The Xylose absorption test is a common medical exam often
done to identify digestive disorders that exhibit symptoms of malabsorption of
the distal small intestine due to structural defects in the mucosal integrity
of the stomach's intestinal mucosa. D-Xylose is an artificial sugar, or
monosaccharide that doesn't require specific enzymes for complete absorption
before entering the bloodstream. Malabsorption occurs when there is a reduced
permeability of the small intestine into the bloodstream.
In the absence of specialized and accurate blood tests, this
sugar cannot be absorbed by the bloodstream and may produce symptoms of
hypoglycemia such as dizziness, fainting, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Because of the difficulty in diagnosing the exact cause of this condition, Xylose
absorption test is done to identify potentially serious digestive
disorders. Geriatric people are more prone to malabsorption as they have less
capability of absorbing carbohydrates and other nutrients.
Thus, with the increasing geriatric population, the demand
for xylose absorption test is also increasing. According to the World Health Organization
(WHO), the world's population aged 60 years and older is expected to total 2
billion by 2050. Japan has the highest proportion of elderly citizens of any
country in the world. In 2019, the population aged 65 years and above in Japan
accounted for around 28% of the total Japanese population, and is expected to
increase by 10% (to 38%) Japan by 2060.



Comments
Post a Comment